Quick jump |
Encryption allows you to encrypt important data in the database, such as credit card numbers or Social Security Numbers. You need to select the encryption method, enter the encryption key, and choose the fields to be encrypted.
Note: the Encryption feature is available only in the Enterprise Edition of PHPRunner. See Editions Comparison.
Press the Encryption button on the Security screen to open the Encryption popup.
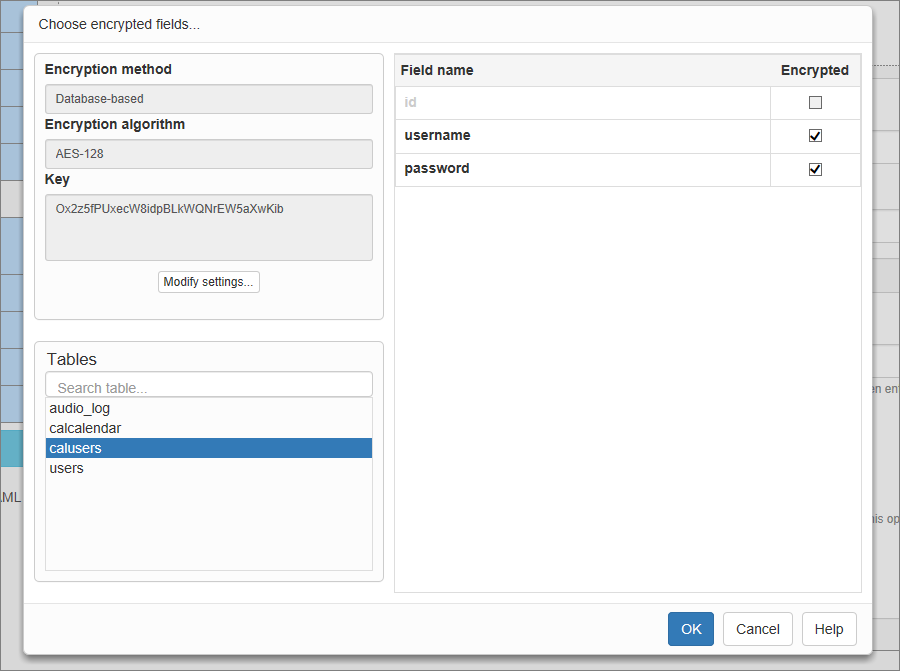
You can select a Database-based or Code-based encryption method.
Note: the Database-based encryption method is available only for MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and MS SQL Server databases.
The Database-based method is preferable since it has more features than the Code-based method. With the Database-based encryption, for example, the encrypted fields can be sorted and grouped, the search offers suggestions and includes all operators (CONTAINS, EQUALS, MORE THAN, etc.).
Database-based encryption requirements
PostgreSQL:
•install the pgcrypto module.
Oracle:
•give users full rights to the SYS.DBMS_CRYPTO package;
•the Oracle version must be 10 or higher.
MySQL:
•enable SSL support.
Code-based encryption requirements
To use the PHP encryption, enable the mcrypt extension in php.ini (PHP 5.3 and higher includes this extension by default).
We recommend using the encryption key that is at least 10 characters long. You can also use the Generate button to generate a random key.
PHPRunner can encrypt only text fields. Since the encrypted value usually is at least 2-3 times longer than source value, you should choose the maximum length fields such as TEXT in MySQL or MEMO in MS Access.
Note: PHPRunner does not encrypt the existing data. Encryption is applied to the record during the Add/Edit operations.
Note: once the encrypted data is stored in the database, you should not change the encryption type and key, or deactivate the encryption, as the data will remain encrypted.
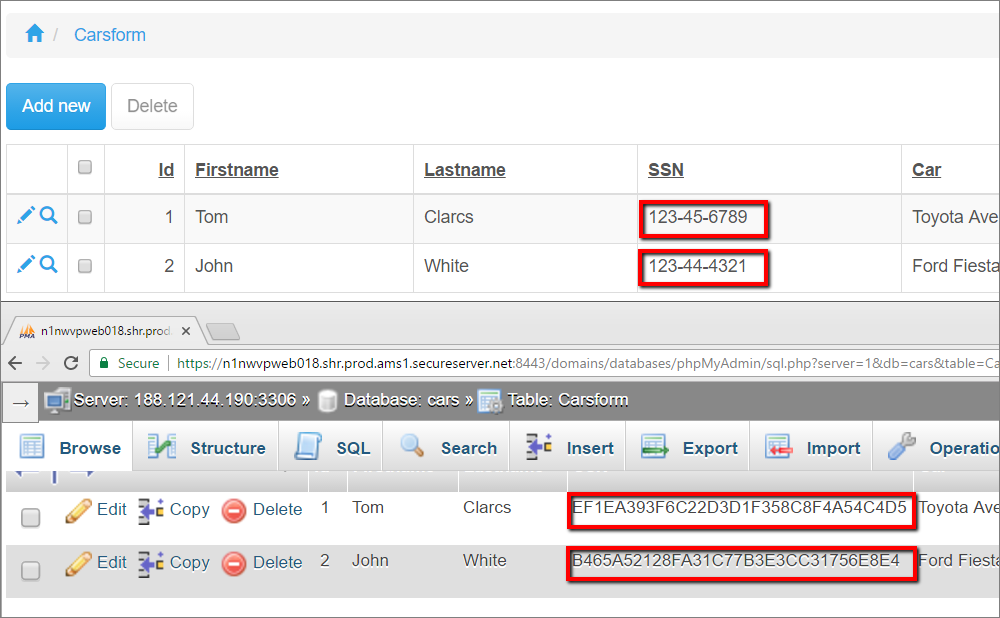
Here is an example of encrypted data in the application:
Functions used for database-based encryption
Oracle:
•Encryption: DBMS_CRYPTO.ENCRYPT()
•Decryption: DBMS_CRYPTO.DECRYPT()
MS SQL Server:
•Encryption: EncryptByPassPhrase(), EncryptByKey()
•Decryption: DecryptByPassPhrase(), DecryptByKey()
MySQL:
•Encryption: DES_ENCRYPT(), AES_ENCRYPT()
•Decryption: DES_DECRYPT(), AES_DECRYPT()
PostgreSQL:
•Encryption: pgp_sym_encrypt()
•Decryption: pgp_sym_decrypt()
Functions used for code-based encryption
PHPRunner uses DES or AES-128 encryption algorithms.
Encrypting the existing data in the database
Note:
1. Before starting this procedure, make a backup of the database!
2. You may encrypt the existing values only once. We do not recommend double encryption as it causes problems with decryption.
3. After the encryption, it Is not always possible tell whether the data had been encrypted or not.
1. Before enabling encryption export your table data to CSV or Excel
2. Turn on the encryption
3. If this table has key columns selected, simply import the data back. It will update the existing data with encrypted values.
4. If this table doesn't have key columns selected then delete all the data first and then run the import.
MySQL, AES encryption
The key variable should contain the encryption key specified in PHPRunner on the Encryption screen.
//define encryption key
$key='09a308862fbe462095dd6eba33ab9dd21b8fd35b0d884b48819a34ce8636983b';
$sql = "SELECT cast(AES_DECRYPT(unhex(customer_name), '".$key."') as char) AS custname FROM customers_table WHERE id = 'CUST123'";
$rs = CustomQuery($sql);
$data = db_fetch_array($rs);
echo $data["custname"];
More about security:
•CAPTCHA on authentication pages
See also: